Geostationary Satellite Orbit Distance From Earth
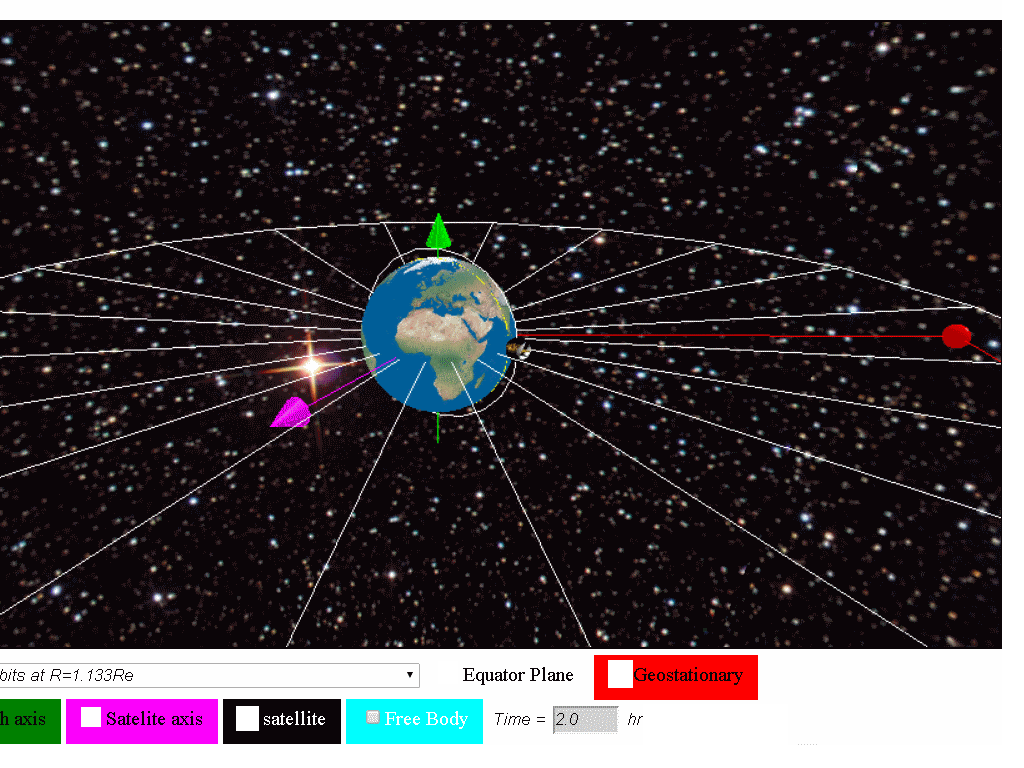
At any inclination a geosynchronous orbit synchronizes with the rotation of the earth.
Geostationary satellite orbit distance from earth. The first lagrange point is located between the earth and the sun giving satellites at this point a constant view of the sun. Located at 22 236 miles 35 786 kilometers above earth s equator this position is a valuable spot. This particular orbit is. The solar and heliospheric observatory soho a nasa and european space agency satellite tasked to monitor the sun orbits the first lagrange point about 1 5 million kilometers away from earth.
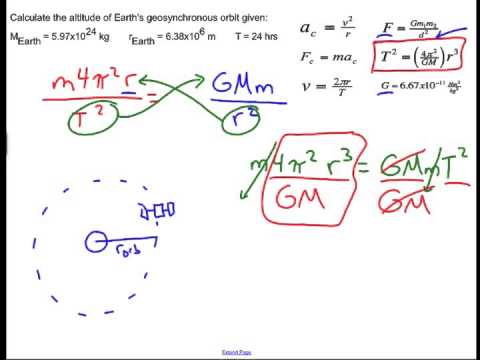
Which converts to about 22 300 miles. Typically the orbit of a medium earth orbit satellite is about 16 000 kilometres 10 000 mi above earth. From the center of the earth this is approximately 42 164 kilometers. This is in contrast to the geostationary orbit where satellites are always 35 786 kilometres 22 236 mi from the earth.
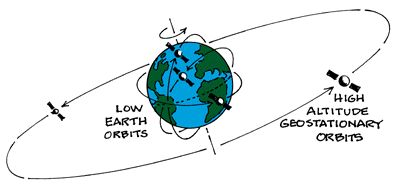
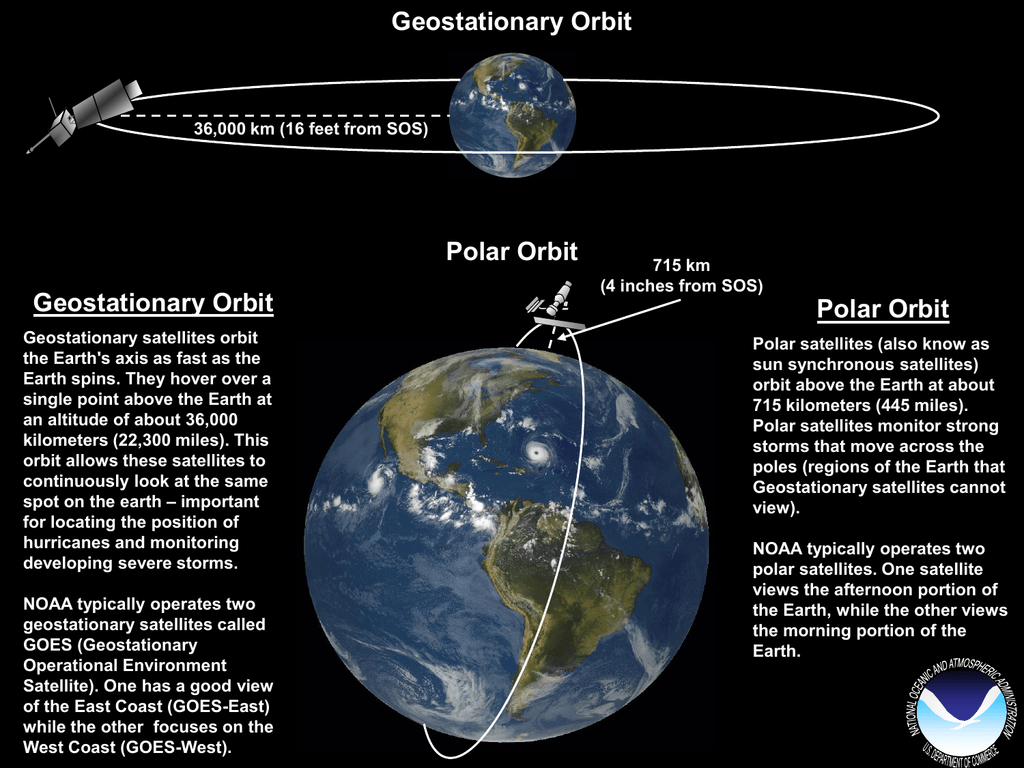
About 35 786 kilometers above the earth s surface satellites are in geostationary orbit. An earth orbiting satellite s motion is mostly controlled by earth s gravity. This is the distance the satellite needs to be from the center of the earth. Like leos these satellites do not maintain a stationary distance from the earth.
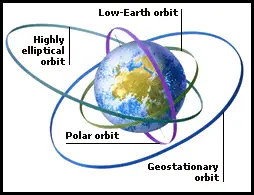
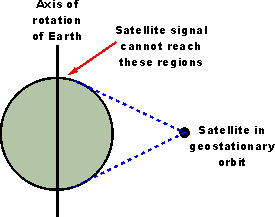
This is the distance from the surface of the earth geosynchronous satellites need to orbit. A reasonably small 4 8 m asteroid recently flew by earth passing close to satellites orbiting in the geostationary ring at a distance of about 42 735 km from earth s centre and only about 1200 km. Geostationary orbit a circular orbit 35 785 km 22 236 miles above earth s equator in which a satellite s orbital period is equal to earth s rotation period of 23 hours and 56 minutes. 156 a satellite in such an orbit is at an altitude of approximately 35 786 km 22 236 mi above mean sea level.
This distance puts it in the high earth orbit category. A spacecraft in this orbit appears to an observer on earth to be stationary in the sky. Subtracting the earth s radius of. At this distance they orbit the earth at the same rate the earth is turning which means.
The second lagrange point is about the same distance from the earth but. A geostationary orbit also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit geo is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35 786 kilometres 22 236 miles above earth s equator and following the direction of earth s rotation. An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to the earth s rotational period one sidereal day and so to ground observers it appears motionless in a fixed. It maintains the same.
A geostationary equatorial orbit geo is a circular geosynchronous orbit in the plane of the earth s equator with a radius of approximately 42 164 km 26 199 mi measured from the center of the earth.